Commentary by Adam Sieminski, KAPSARC President
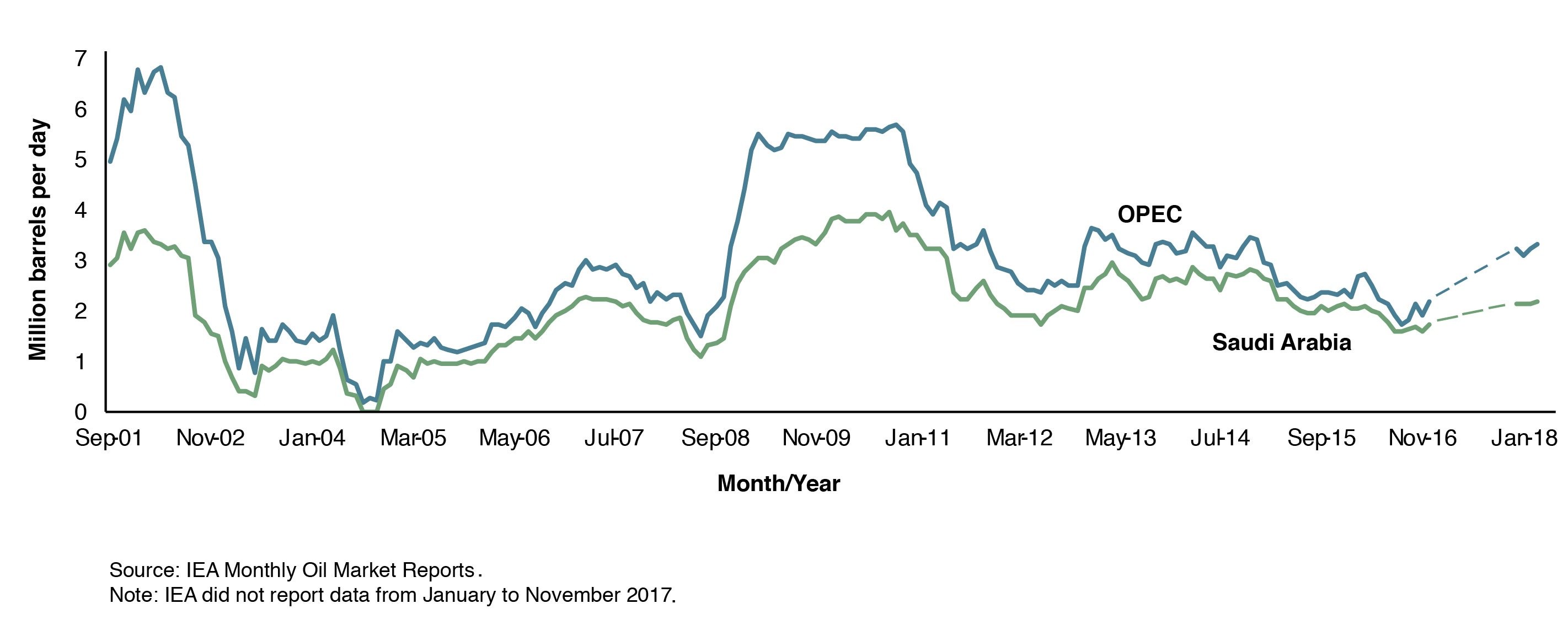
Rising international oil prices and increased geopolitical uncertainty have put OPEC’s spare production capacity back into the spotlight. KAPSARC’s recent peer-reviewed collaborative study in the Energy Journal by authors Axel Pierru, James L. Smith, and Tamim Zamrik finds that OPEC’s spare capacity reduces oil price volatility and generates between $170 and $200 billion of annual economic benefits for the global economy.Investments in spare capacity provide value to the economy because deploying the production held in response to disruptions saves costs that result from price volatility. This value can be calculated by subtracting the gross domestic profit (GDP) losses that the world would expect to suffer even after deploying the spare capacity buffer from the expected losses without the buffer. The expected losses depend on the buffer size, the magnitude and persistence of the shocks, and on the global GDP losses incurred when there are production shortfalls.For many years analysts have judged oil market stability by considering the level of excess production capacity maintained almost exclusively by OPEC. The production and delivery of oil to the market is subject to frequent disruptions, whether from conflicts, natural disasters, labor strikes, port closures, or political sanctions. In addition, demand can be affected by other factors such as the general state of the global economy. The rigidity of demand and supply magnifies the impact of any disruption, and restoring equilibrium to the market often requires sharp price movements, especially in the short term.These sharp movements and the financial risk premium associated with volatility impose costs on the global economy if they are not dampened through mechanisms including the release of strategic stocks held by major oil importers, redirection of oil tankers to fill geographical imbalances, or increases in production from OPEC spare capacity. Historical examples where OPEC has used its spare capacity to stabilize the market include increasing members’ production to meet the unexpected buildup of global oil demand from 2003-2004, and to compensate for the collapse of Libya’s oil production following the uprising of 2011.Figure 1 shows the change in monthly ‘effective’ spare capacity reported by the International Energy Agency (IEA) since 2001. OPEC’s spare capacity amounted to 3.24 million barrels per day in June 2018, with world oil demand forecast to reach 100 million barrels per day by the end of the year. Saudi Arabia has held, on average, 70 percent of OPEC’s total spare capacity since 2001.Figure 1. OPEC’s effective spare capacity
 The study uses monthly data to build and estimate a model to analyze a ‘counterfactual’ scenario — comparing what would have been the outcome if OPEC had not deployed spare capacity to the actual outcome observed in global oil markets. The model describes how OPEC maintains a buffer of spare capacity that it uses to offset perceived shocks to global oil demand and supply. The analysis of OPEC’s behavior recognizes that the economic, industrial or geopolitical information necessary to accurately judge the size of such shocks is never fully available, which limits OPEC’s ability to stabilize the price of oil. In addition, the model accounts for OPEC’s logistical constraints and compliance levels.The counterfactual scenario is based on estimates of the monthly oil prices that would have prevailed from 2005 to 2014 had OPEC not used its spare capacity to offset shocks. These hypothetical prices are compared to the prices historically observed. There is no consensus on how price responsive global demand is. The study examines the effects of a range of monthly price elasticity estimates. Figure 2, based on a monthly price elasticity of -1 percent, is representative of the type of impact that OPEC’s spare capacity policy has had. The analysis indicates that OPEC had a substantial stabilizing influence, perhaps reducing oil price volatility by as much as half. The same conclusion holds when the analysis only considers Saudi Arabia, or the four GCC members of OPEC collectively. Indeed, the analysis finds that Saudi Arabia has played a greater role in offsetting shocks than all other OPEC members combined.Figure 2: OPEC's spare capacity reduces oil price volatility
The study uses monthly data to build and estimate a model to analyze a ‘counterfactual’ scenario — comparing what would have been the outcome if OPEC had not deployed spare capacity to the actual outcome observed in global oil markets. The model describes how OPEC maintains a buffer of spare capacity that it uses to offset perceived shocks to global oil demand and supply. The analysis of OPEC’s behavior recognizes that the economic, industrial or geopolitical information necessary to accurately judge the size of such shocks is never fully available, which limits OPEC’s ability to stabilize the price of oil. In addition, the model accounts for OPEC’s logistical constraints and compliance levels.The counterfactual scenario is based on estimates of the monthly oil prices that would have prevailed from 2005 to 2014 had OPEC not used its spare capacity to offset shocks. These hypothetical prices are compared to the prices historically observed. There is no consensus on how price responsive global demand is. The study examines the effects of a range of monthly price elasticity estimates. Figure 2, based on a monthly price elasticity of -1 percent, is representative of the type of impact that OPEC’s spare capacity policy has had. The analysis indicates that OPEC had a substantial stabilizing influence, perhaps reducing oil price volatility by as much as half. The same conclusion holds when the analysis only considers Saudi Arabia, or the four GCC members of OPEC collectively. Indeed, the analysis finds that Saudi Arabia has played a greater role in offsetting shocks than all other OPEC members combined.Figure 2: OPEC's spare capacity reduces oil price volatility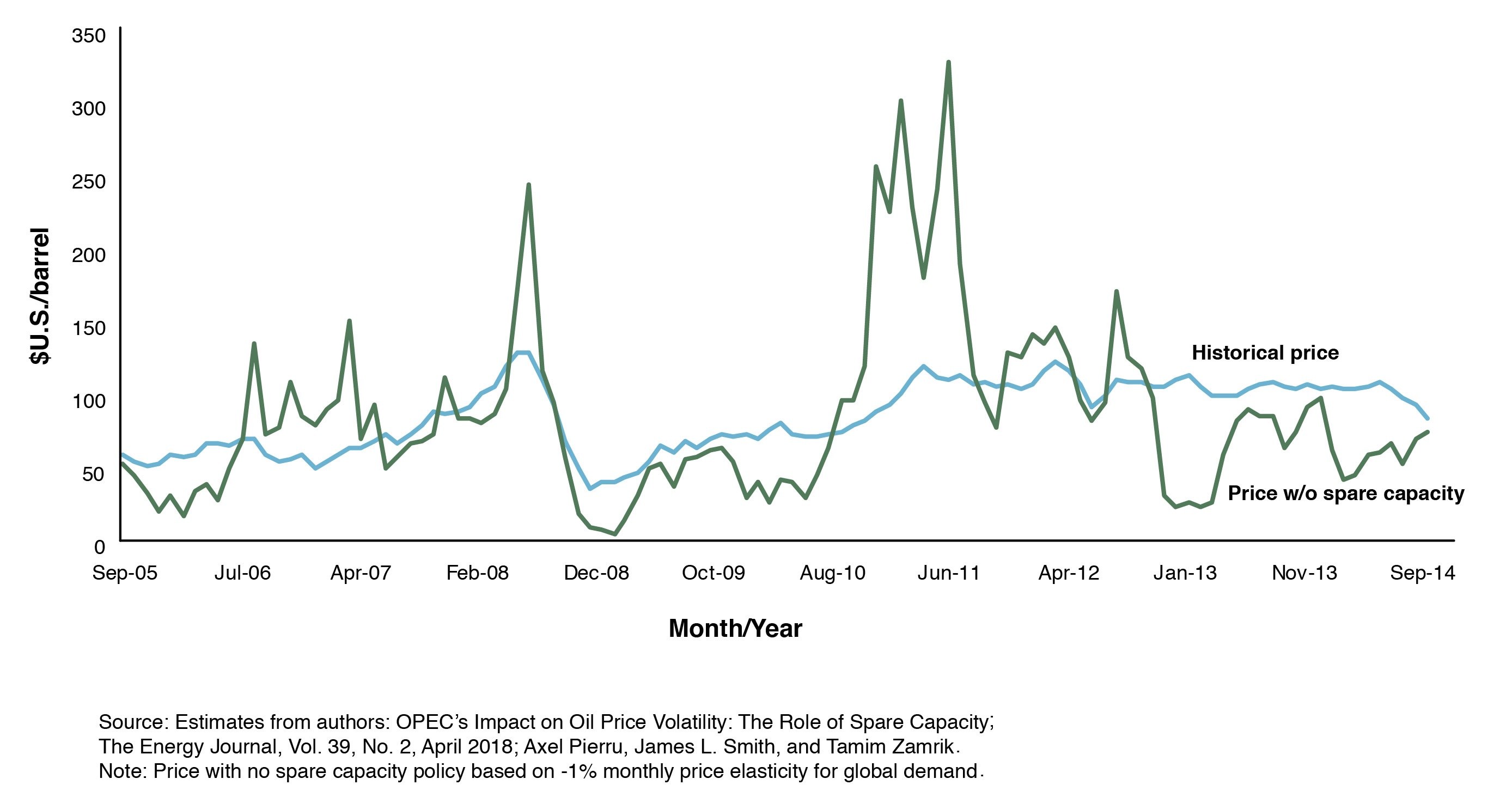 The study also examines the magnitude of spare capacity. This is especially relevant given that the absolute level of spare capacity is now less than it was two decades ago, despite oil demand having grown by 25 percent. To estimate the desired size of the buffer, the study attempts to consider all possible shocks and their respective likelihoods, and then compare the value of spare capacity to the cost of building it. The ‘right size’ is when the cost of adding a marginal barrel per day of capacity is equal to the GDP loss that would arise without that additional barrel of capacity. The analysis confirms that OPEC’s buffer, estimated at 2.64 million barrels per day (1.94 million barrels per day for Saudi Arabia), has been in line with global macroeconomic needs.Spare capacity is only one piece of a much larger picture in terms of neutralizing the negative impact of oil shocks. By maintaining costly inventories, individual consumers, producers, government agencies, and multilateral organizations also shoulder part of the burden of dealing with oil price shocks. This has not been entirely altruistic because spare capacity has a value to the holders: production from the buffer is typically put on the market when prices are high.The recent emergence of shale oil as the world’s marginal producer, with a development lead time measured in months, has made non-OPEC supply much more reactive to price. By contributing to market stability, shale oil is capturing a share of the historical value of spare capacity for the world economy and reducing the incentive for OPEC members to invest in maintaining the cushion. However, shale oil is also subject to potential logistical constraints, such as those currently limiting its expansion in West Texas. Furthermore, it does not suffice to rapidly offset unanticipated shocks of large magnitude. As such, it does not provide sufficient protection for the world economy and OPEC spare capacity still provides value in stabilizing oil markets.
The study also examines the magnitude of spare capacity. This is especially relevant given that the absolute level of spare capacity is now less than it was two decades ago, despite oil demand having grown by 25 percent. To estimate the desired size of the buffer, the study attempts to consider all possible shocks and their respective likelihoods, and then compare the value of spare capacity to the cost of building it. The ‘right size’ is when the cost of adding a marginal barrel per day of capacity is equal to the GDP loss that would arise without that additional barrel of capacity. The analysis confirms that OPEC’s buffer, estimated at 2.64 million barrels per day (1.94 million barrels per day for Saudi Arabia), has been in line with global macroeconomic needs.Spare capacity is only one piece of a much larger picture in terms of neutralizing the negative impact of oil shocks. By maintaining costly inventories, individual consumers, producers, government agencies, and multilateral organizations also shoulder part of the burden of dealing with oil price shocks. This has not been entirely altruistic because spare capacity has a value to the holders: production from the buffer is typically put on the market when prices are high.The recent emergence of shale oil as the world’s marginal producer, with a development lead time measured in months, has made non-OPEC supply much more reactive to price. By contributing to market stability, shale oil is capturing a share of the historical value of spare capacity for the world economy and reducing the incentive for OPEC members to invest in maintaining the cushion. However, shale oil is also subject to potential logistical constraints, such as those currently limiting its expansion in West Texas. Furthermore, it does not suffice to rapidly offset unanticipated shocks of large magnitude. As such, it does not provide sufficient protection for the world economy and OPEC spare capacity still provides value in stabilizing oil markets.This commentary is based on a KAPSARC research project initiated in late 2016, resulting in the April 2018 publication of the paper 'OPEC’s Impact on Oil Price Volatility: The Role of Spare Capacity' in the Energy Journal, Vol. 39, No. 2, 2018.
تعليق السيد/ آدم سيمنسكي رئيس مركز الملك عبدالله للدراسات والبحوث البترولية
الأسعار الدولية المتصاعدة للنفط والضبابية الجيوسياسية أديا الى إعادة وضع الطاقة الإنتاجية الاحتياطية للأوبك على جدول أعمال السوق العالمية. وجدت دراسة أجراها كابسارك مؤخرًا أن الطاقة الإنتاجية الاحتياطية لأوبك تحد من تقلبات أسعار النفط وتحقيق فوائد للاقتصاد العالمي تتراوح بين 170-200 مليار دولا سنويًا.الاستثمارات في الطاقة الاحتياطية ذات قيمة للاقتصاد العالمي، ذلك أن زيادة الانتاج استجابة لحدوث انقطاعات في الإمدادات يوفر التكاليف الناتجة عن تقلبات الأسعار. ويمكن احتساب هذه القيمة بالنظر للفارق بين الخسائر المتوقعة للناتج الإجمالي المحلي بعد استخدام الطاقة الاحتياطية والخسائر المتوقعة لو لم يوجد هذا الاحتياطي. ويعتمد حجم الخسائر على حجم الطاقة الاحتياطية ومدى قوة صدمات الأسعار وخسائر الناتج المحلي الإجمالي المتكبدة جراء حدوث قصور في الإنتاج.ظل المحللون لسنوات يحكمون على استقرار السوق بالنظر إلى مستوى الطاقة الإنتاجية الفائضة التي تحتفظ بها أوبك حيث يتعرض إنتاج النفط وإيصاله للسوق إلى اضطرابات متكررة، سواء بسبب النزاعات أو الكوارث الطبيعية أو إضرابات العمال أو إغلاق الموانئ أو العقوبات السياسية. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، قد يتأثر الطلب بعوامل أخرى مثل الحالة العامة للاقتصاد العالمي. إن جمود الطلب والعرض يزيد من تأثير أي اضطراب، وغالباً ما تتطلب استعادة التوازن للسوق تحرّكات حادة في الأسعار، خاصة على المدى القصير. هذه التحركات والمخاطر المالية المرتبطة بتقلب الأسعار تفرض تكاليف على الاقتصاد العالمي إذا لم يتم تقليلها من خلال آليات كاستخدام المخزونات الاستراتيجية التي يحتفظ بها كبار مستوردي النفط، وإعادة توجيه ناقلات النفط لمعالجة الاختلالات الجغرافية أو زيادة الإنتاج باستخدام طاقة أوبك الاحتياطية. وتشمل الأمثلة التاريخية لاستخدام أوبك طاقتها الاحتياطية للعمل على استقرار السوق زيادة الدول الأعضاء إنتاجها لتلبية الزيادة غير المتوقعة في الطلب العالمي على النفط من 2003-2004، والتعويض عن انهيار إنتاج النفط الليبي في أعقاب الاضطرابات التي اندلعت عام 2011. ويبين الشكل 1 التغير في الطاقة الاحتياطية الشهرية "الفعالة" وفق الوكالة الدولية للطاقة منذ عام 2001. وبلغت الطاقة الاحتياطية الفعالة لمنظمة أوبك 3.24 مليون برميل في اليوم في يونيو 2018، مع توقع أن يصل الطلب العالمي على النفط إلى 100 مليون برميل في اليوم بنهاية العام. وقد احتفظت المملكة العربية السعودية بما متوسطه 70 في المائة من الطاقة الاحتياطية الإجمالية لمنظمة أوبك منذ عام 2001.
 الشكل 1: الطاقة الاحتياطية الفعالة (المصدر: تقارير أسواق النفط الصادرة عن الوكالة الدولية للطاقة).ملحوظة: لا توفر الوكالة الدولية للطاقة تقارير عن البيانات من يناير إلى نوفمبر 2017.تستخدم الدراسة بيانات شهرية لبناء وتقدير نموذج لتحليل سيناريو "مغاير" - لمقارنة ما كان يمكن أن تكون النتيجة لو لم تقم أوبك باستخدام طاقة احتياطية على النتيجة الفعلية الملاحظة على أسواق النفط العالمية. يصف النموذج كيف تحافظ أوبك على طاقة احتياطية تستخدمها للتصدي للصدمات على جانبي العرض والطلب العالميين. ويظهر تحليل سلوك أوبك أن المعلومات الاقتصادية والصناعية أو الجيوسياسية اللازمة لحكم دقيق على حجم هذه الصدمات ليست متاحة بالكامل، مما يحد من قدرة أوبك على موازنة سعر النفط. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يأخذ النموذج في الاعتبار القيود اللوجستية ومستويات الامتثال لأوبك.يستند السيناريو المغاير إلى تقديرات أسعار النفط الشهرية التي كانت لتسود في الفترة من 2001 إلى 2014 لو لم تستخدم أوبك طاقتها الاحتياطية لموازنة الصدمات. تتم مقارنة هذه الأسعار الافتراضية بالأسعار التي تم تتبعها تاريخيًا. ولايوجد إجماع حول مدى استجابة الطلب العالمي للأسعار. يمثل الشكل-2 أحد آثار سياسة الطاقة الاحتياطية لأوبك وفق مرونة أسعار عند -1 في المائة. ويشير التحليل إلى أن لمنظمة أوبك تأثير كبير على الاستقرار، وقد تقلل من تقلب أسعار النفط بمقدار النصف. ويظهر نفس الاستنتاج عند إجراء التحليل على المملكة العربية السعودية لوحدها، أو دول مجلس التعاون الخليجي الأربع أعضاء أوبك. ووجد التحليل أن المملكة العربية السعودية لعبت دوراً أكبر في امتصاص الصدمات مقارنة بأعضاء أوبك الآخرين مجتمعين.
الشكل 1: الطاقة الاحتياطية الفعالة (المصدر: تقارير أسواق النفط الصادرة عن الوكالة الدولية للطاقة).ملحوظة: لا توفر الوكالة الدولية للطاقة تقارير عن البيانات من يناير إلى نوفمبر 2017.تستخدم الدراسة بيانات شهرية لبناء وتقدير نموذج لتحليل سيناريو "مغاير" - لمقارنة ما كان يمكن أن تكون النتيجة لو لم تقم أوبك باستخدام طاقة احتياطية على النتيجة الفعلية الملاحظة على أسواق النفط العالمية. يصف النموذج كيف تحافظ أوبك على طاقة احتياطية تستخدمها للتصدي للصدمات على جانبي العرض والطلب العالميين. ويظهر تحليل سلوك أوبك أن المعلومات الاقتصادية والصناعية أو الجيوسياسية اللازمة لحكم دقيق على حجم هذه الصدمات ليست متاحة بالكامل، مما يحد من قدرة أوبك على موازنة سعر النفط. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يأخذ النموذج في الاعتبار القيود اللوجستية ومستويات الامتثال لأوبك.يستند السيناريو المغاير إلى تقديرات أسعار النفط الشهرية التي كانت لتسود في الفترة من 2001 إلى 2014 لو لم تستخدم أوبك طاقتها الاحتياطية لموازنة الصدمات. تتم مقارنة هذه الأسعار الافتراضية بالأسعار التي تم تتبعها تاريخيًا. ولايوجد إجماع حول مدى استجابة الطلب العالمي للأسعار. يمثل الشكل-2 أحد آثار سياسة الطاقة الاحتياطية لأوبك وفق مرونة أسعار عند -1 في المائة. ويشير التحليل إلى أن لمنظمة أوبك تأثير كبير على الاستقرار، وقد تقلل من تقلب أسعار النفط بمقدار النصف. ويظهر نفس الاستنتاج عند إجراء التحليل على المملكة العربية السعودية لوحدها، أو دول مجلس التعاون الخليجي الأربع أعضاء أوبك. ووجد التحليل أن المملكة العربية السعودية لعبت دوراً أكبر في امتصاص الصدمات مقارنة بأعضاء أوبك الآخرين مجتمعين.  الشكل-2 الطاقة الاحتياطية لأوبك تحد من تقلبات الأسعارالمصدر: تقديرات أكسل بيرو – يوليو 2018ملاحظة: تفترض الاسعار بلا سياسة للطاقة الاحتياطية مرونة اسعار شهريو 1% للطلب العالميتتقصى الدراسة كذلك حجم الطاقة الإنتاجية الاحتياطية لأوبك. وهذا مهم نظرًا لأن للطاقة الاحتياطية الآن أقل مما كانت عليه قبل عقدين من الزمن على الرغم من نمو الطلب على النفط بنسبة 25 في المائة. ولتقدير الحجم الملائم للطاقة الاحتياطية تحاول الدراسة النظر في كل صدمات الاسعار الممكن حدوثها، ثم تقارن قيمة الطاقة الاحتياطية بتكلفة بنائها. "الحجم الصحيح" هو عندما تكون تكلفة إضافة برميل هامشي للطاقة الاحتياطية في اليوم مساوية لخسارة الناتج المحلي الإجمالي التي ستنشأ بدون ذلك البرميل الإضافي. يؤكد التحليل أن مخفف الصدمة لمنظمة أوبك المقدر بـ 2.64 مليون برميل يوميًا (1.9 برميل منها من المملكة) يتماشى مع احتياجات الاقتصاد الكلي العالمي. الطاقة الاحتياطية ليست سوى قطعة واحدة من صورة أكبر بكثير للحد من تأثير صدمات الأسعار النفطية. يتحمل المستهلكون الأفراد والمنتجون والجهات الحكومية والمنظمات المتعددة الأطراف أيضاً جزءًا من عبء التعامل مع صدمات أسعار النفط جراء الاحتفاظ بالمخزونات المكلفة. بالتأكيد لا يحصل هذا دون مقابل حيث تحقق الطاقة الإنتاجية الإضافية فوائد مالية تأتي من أن تلك الكميات من النفط تضخ وتباع وفق أسعار مرتفعة.إن ظهور النفط الصخري مؤخراً جعل العرض من غير أعضاء أوبك أكثر استجابة للأسعار. وبمساهمته في استقرار السوق، يستحوذ النفط الصخري على حصة من القيمة التاريخية للطاقة الاحتياطية للاقتصاد العالمي ويقلل من الحافز لأعضاء أوبك للاستثمار في الحفاظ على مخفف الصدمة، غير أن النفط الصخري بدوره يخضع لقيود لوجستية كتلك التي تحد مؤقتًا من توسعه في حوض بيرميان غرب تكساس. كما أنه لا يمكن للنفط الصخري امتصاص الصدمات الكبيرة غير المتوقعة، وبالتالي فهو لا يوفر نفس القدر من الحماية والاستقرار للاقتصاد العالمي كالذي توفره الطاقة الاحتياطية لمنظمة الأوبك.بني هذا التعليق على المشروع البحثي الذي بدأ أواخر عام 2016 وأسفر عن دراسة نشرت في إبريل هذا العام في المجلة المتخصصة بالطاقة انيرجي جورنال بعنوان "أثر أوبك على تقلبات الاسعار: دور الطاقة الاحتياطية"
الشكل-2 الطاقة الاحتياطية لأوبك تحد من تقلبات الأسعارالمصدر: تقديرات أكسل بيرو – يوليو 2018ملاحظة: تفترض الاسعار بلا سياسة للطاقة الاحتياطية مرونة اسعار شهريو 1% للطلب العالميتتقصى الدراسة كذلك حجم الطاقة الإنتاجية الاحتياطية لأوبك. وهذا مهم نظرًا لأن للطاقة الاحتياطية الآن أقل مما كانت عليه قبل عقدين من الزمن على الرغم من نمو الطلب على النفط بنسبة 25 في المائة. ولتقدير الحجم الملائم للطاقة الاحتياطية تحاول الدراسة النظر في كل صدمات الاسعار الممكن حدوثها، ثم تقارن قيمة الطاقة الاحتياطية بتكلفة بنائها. "الحجم الصحيح" هو عندما تكون تكلفة إضافة برميل هامشي للطاقة الاحتياطية في اليوم مساوية لخسارة الناتج المحلي الإجمالي التي ستنشأ بدون ذلك البرميل الإضافي. يؤكد التحليل أن مخفف الصدمة لمنظمة أوبك المقدر بـ 2.64 مليون برميل يوميًا (1.9 برميل منها من المملكة) يتماشى مع احتياجات الاقتصاد الكلي العالمي. الطاقة الاحتياطية ليست سوى قطعة واحدة من صورة أكبر بكثير للحد من تأثير صدمات الأسعار النفطية. يتحمل المستهلكون الأفراد والمنتجون والجهات الحكومية والمنظمات المتعددة الأطراف أيضاً جزءًا من عبء التعامل مع صدمات أسعار النفط جراء الاحتفاظ بالمخزونات المكلفة. بالتأكيد لا يحصل هذا دون مقابل حيث تحقق الطاقة الإنتاجية الإضافية فوائد مالية تأتي من أن تلك الكميات من النفط تضخ وتباع وفق أسعار مرتفعة.إن ظهور النفط الصخري مؤخراً جعل العرض من غير أعضاء أوبك أكثر استجابة للأسعار. وبمساهمته في استقرار السوق، يستحوذ النفط الصخري على حصة من القيمة التاريخية للطاقة الاحتياطية للاقتصاد العالمي ويقلل من الحافز لأعضاء أوبك للاستثمار في الحفاظ على مخفف الصدمة، غير أن النفط الصخري بدوره يخضع لقيود لوجستية كتلك التي تحد مؤقتًا من توسعه في حوض بيرميان غرب تكساس. كما أنه لا يمكن للنفط الصخري امتصاص الصدمات الكبيرة غير المتوقعة، وبالتالي فهو لا يوفر نفس القدر من الحماية والاستقرار للاقتصاد العالمي كالذي توفره الطاقة الاحتياطية لمنظمة الأوبك.بني هذا التعليق على المشروع البحثي الذي بدأ أواخر عام 2016 وأسفر عن دراسة نشرت في إبريل هذا العام في المجلة المتخصصة بالطاقة انيرجي جورنال بعنوان "أثر أوبك على تقلبات الاسعار: دور الطاقة الاحتياطية"
