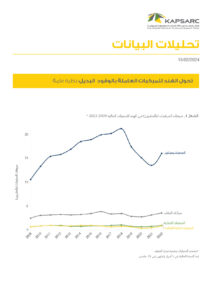
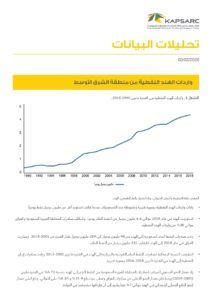
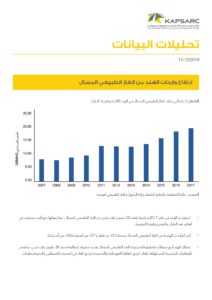
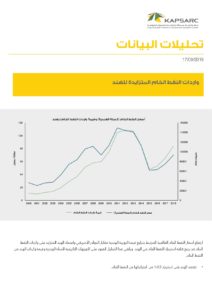
Indian urban infrastructure is in the middle of a massive build-up. For several decades, Indian cities were caught between the demands of an exploding population and the need to provide infrastructure in terms of health, education, transport, and services to meet the core needs of the citizenry. With increasing prosperity and leveraging the strengths of one of the world’s largest and fast-growing economies, Indian policymakers seek to correct their previous underinvestment in city infrastructure. Smart City Mission, Swachh Bharat Mission, and Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation are some of the policy vehicles planned for a broad transformation of India’s urban agenda. This chapter highlights some of the policy initiatives focused on meeting the objectives of Smart Cities. These policy initiatives are expected to help address the current service delivery gap from an urban infrastructure standpoint. By incorporating technology, improving digital access, innovations in traffic management, investments in mobility solutions, and ensuring that the heritage of the Indian cities is maintained, India seeks to answer the challenge of urbanization of millions. These policy mechanisms and the lessons from their successes and failures constitute this chapter’s core. Indian urban infrastructure developments are unique globally, primarily because of the varying range of urbanization across the country, the contextual rationale and the evolving aspirations of the policymakers, and the devolution of developmental powers to local bodies. The Indian experience of implementing the Smart Cities objectives would be unique in the world, given the scale of the massive investments and the millions of citizens whose lives are impacted.
Read Book Chapter
15th أكتوبر 2023