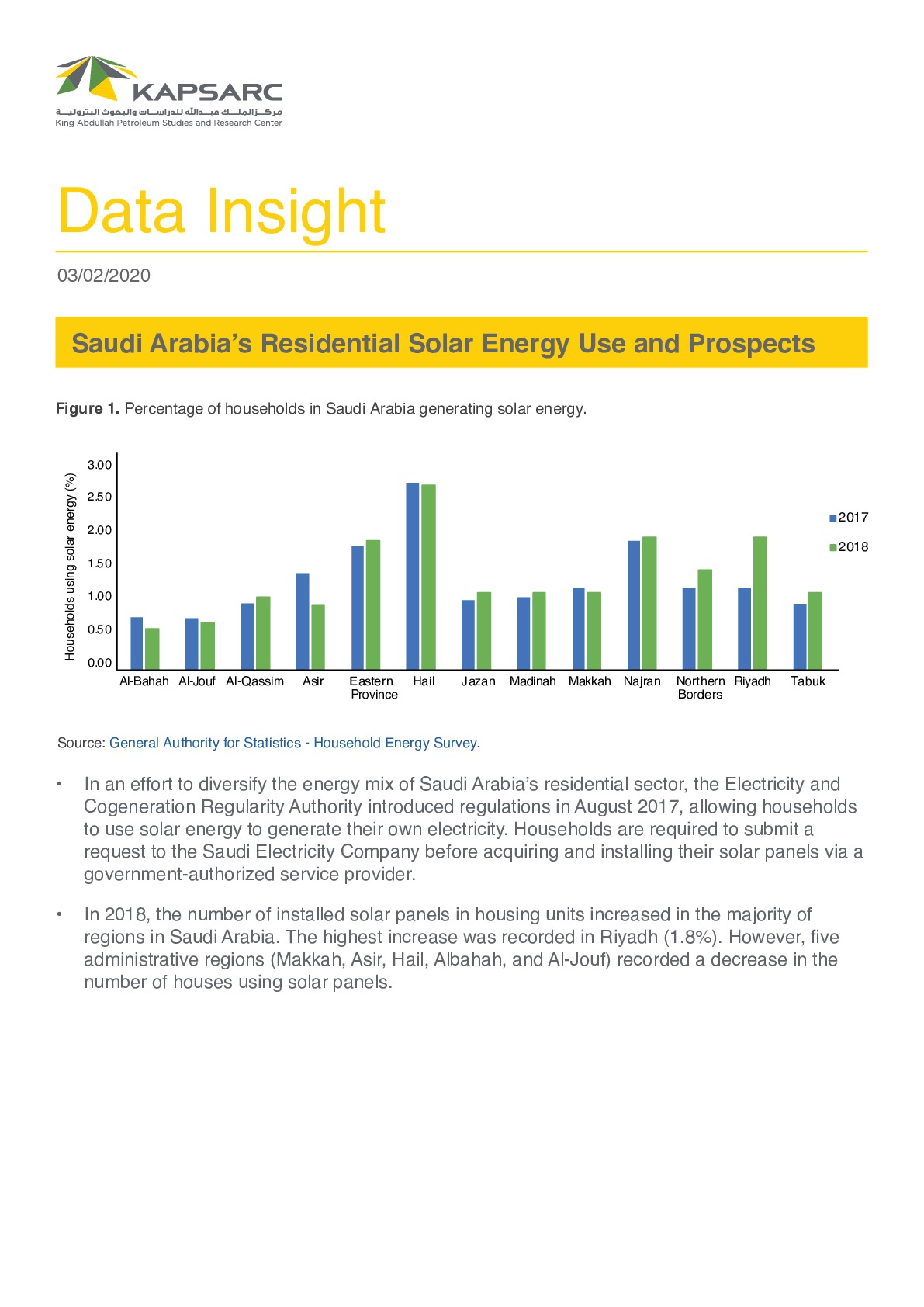
Provides an empirical evaluation of energy trade flows, focusing on crude oil trade among the top 20 crude oil exporters and top 20 crude oil importers. We assess the potential impact of cross-national political disruptions (bilateral and regional) on energy trade between the six producing countries in the GCC and four consuming economies in Northeast Asia. We econometrically measure the impact of political disruptions on total crude oil trade for economies in these two regions to systematically address the question of how much political shocks threaten energy security and the flow of trade. We pay particular attention to how domestic, regional, and international political phenomena and irregular political crises might disrupt energy trade, and under what conditions such disruption might or might not occur. © The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s) 2016.