Solar photovoltaic systems installed on homes and commercial building rooftops are deemed central for a low-carbon future. As capital costs of photovoltaics continue to fall, its role towards making buildings more sustainable and environmentally-friendly will continue to grow. Capital costs of a photovoltaic system comprise the module and balance-of-system costs. The latter refers to everything-else needed to make the photovoltaic system functional including cables, mounts, labor, etc. While modules are priced internationally, the balance-of-system cost is country-specific. Price developments of modules, which have been thoroughly studied in literature, followed an 80% learning curve. Research on the balance-of-system learning curve however, has not been as extensive. In this paper, we estimate for the first time the learning curve of balance-of-system costs in photovoltaics for more than 20 countries via an extensive dataset. Our calculations yield a global learning curve for the balance-of-system of 89%, which corresponds to a progress ratio of 11% compared with 20% for modules. Understanding the rate at which capital costs of photovoltaics are falling with such detail will aid in more effective renewable energy policy planning and budgeting. Finally, some steps requiring no financial commitment but can bring down balance-of-system costs are discussed, which greatly contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. © 2018 The Authors

Executive Director
Dr. Elshurafa is the Executive Director of the Utilities and Renewables Department and possesses 20+ years of experience garnered on…
Dr. Elshurafa is the Executive Director of the Utilities and Renewables Department and possesses 20+ years of experience garnered on three continents. His research interests lie in renewable energy policy, electricity market design and regulation, and power systems modeling. He has led and executed several national modeling initiatives at distributed and utility scales. Some aspects of his research have been adopted by BP in their seminal annual Statistical Review. He is listed among the top 2% scientists globally as per Stanford, and he is a board member of the Saudi Water and Electricity Regulatory Authority. Credited with 50+ papers and patents, he holds a Ph.D. in Engineering and an MBA in Finance.
Expertise
- Renewable Energy Policy
- Electricity Market Design and Regulation
- Power Sector Modeling
Publications See all Amro Elshurafa’s publications
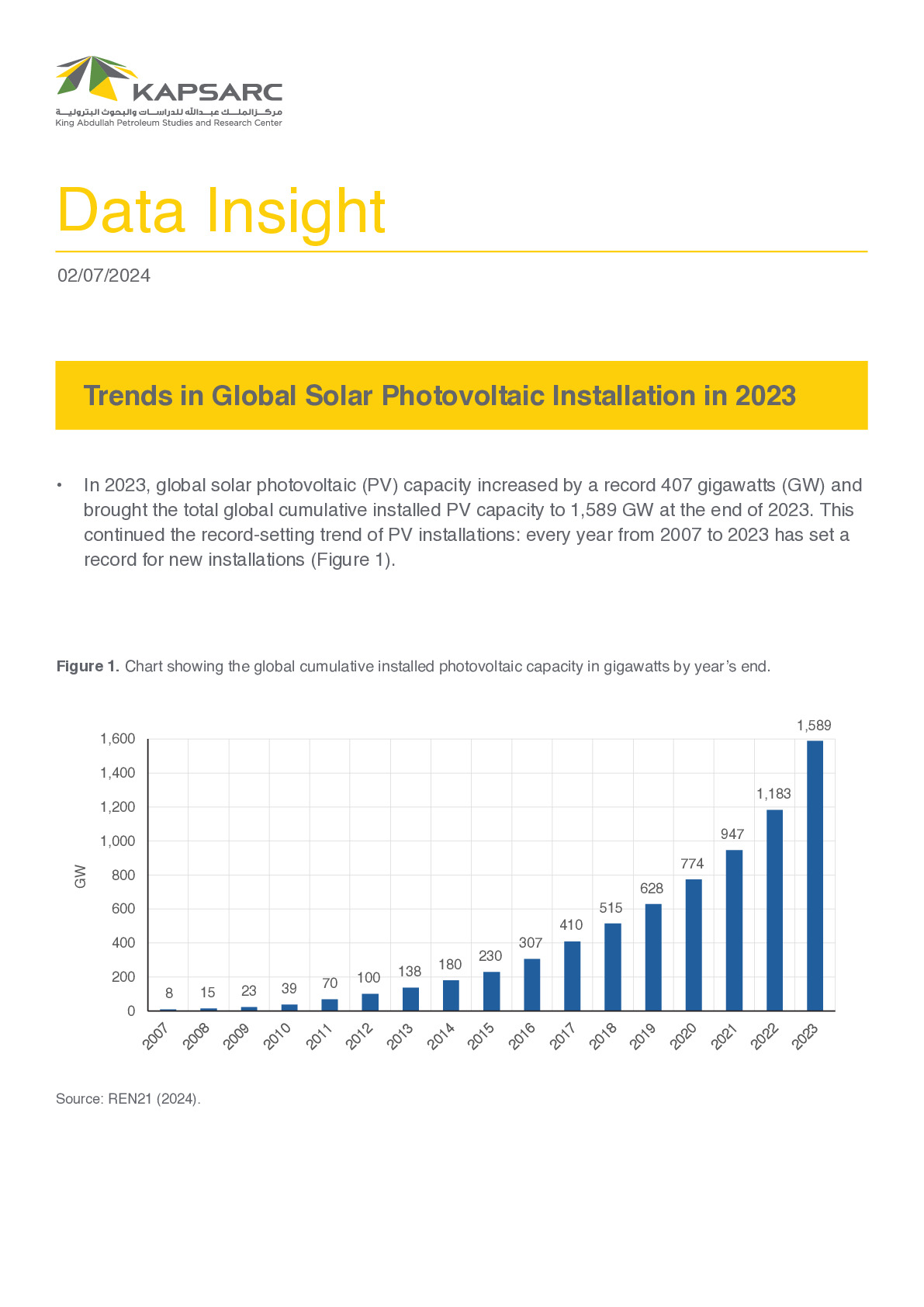
Trends in Global Solar Photovoltaic Installation in 2023
Solar photovoltaic systems installed on homes and commercial building rooftops are deemed central for a…
16th July 2024
Framework for Leveraging the Digitalization of Power Systems within the Context of Energy Transition
Solar photovoltaic systems installed on homes and commercial building rooftops are deemed central for a…
7th July 2024




